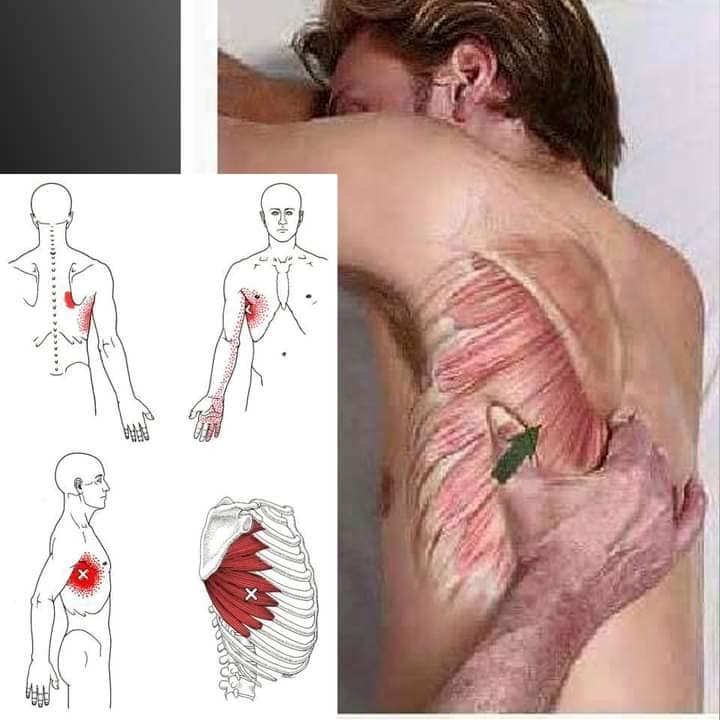
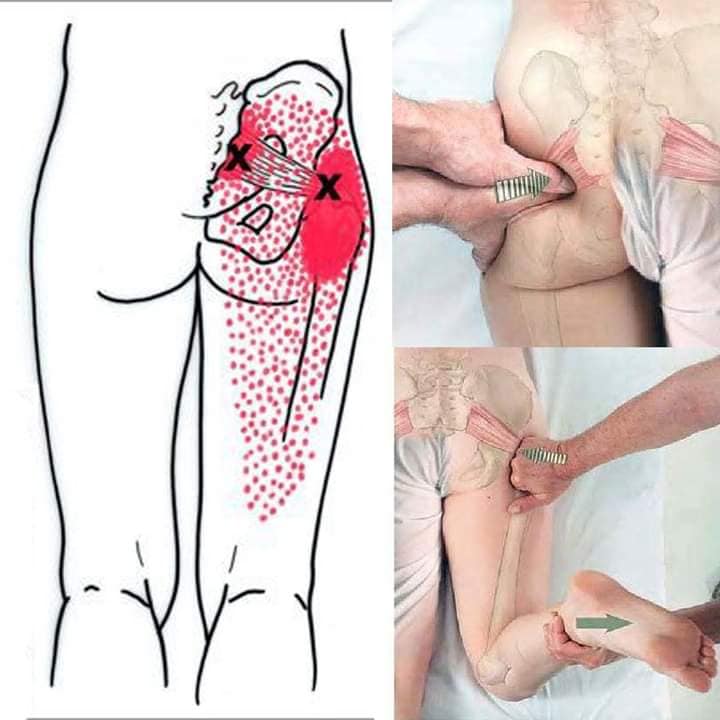
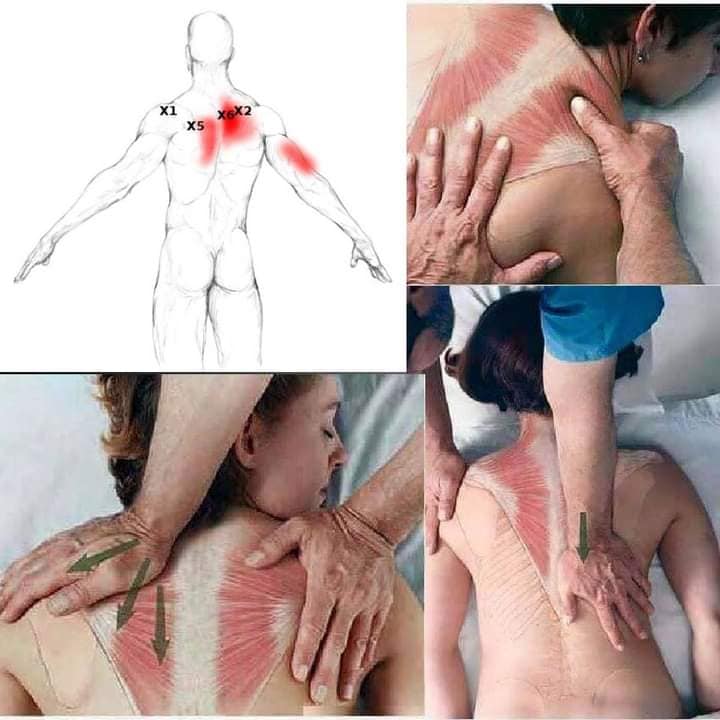
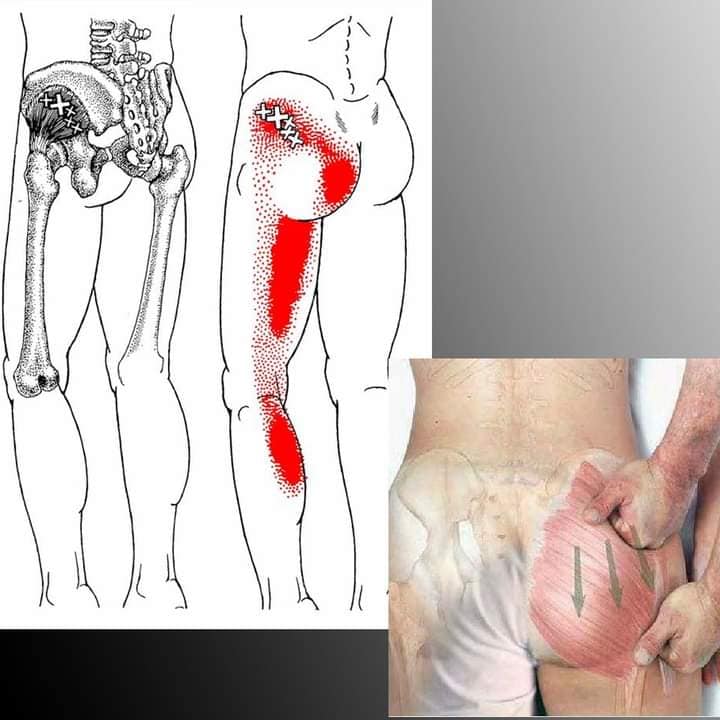
*If you are interested in Dry needling or Acupuncture, please find a licensed practitioner in your area. This is not a instruction on how to do on yourself.
Trigger point Dry needling gets a bad rap from acupuncturists as if Physical Therapists (PT’s) or Chiropractors are stealing or changing acupuncture. In my research, the techniques are not the same.
Some trigger points are in areas around acupoints, but the method of needling is different. There is first palpation and finding the muscles, pinching, and insertion that is very different from acupuncture. I advise all acupuncturists to read the Trigger Point Dry needling book (Jan Dommerholt and Cesar Fernandez De-las-Penas) and watch videos, even take the Myofascial pain seminars to get a clear understanding of this functional medicine.
It does address the muscle-sinew regions in Chinese medicine, however, it is clearly coming from a western anatomy of muscle origin and insertion, function, nerve innervation, referred pain of the trigger point, needling technique and cautions. Here are some notes and videos.
Using and Ai tool to explain: https://youtu.be/v_4xUNukmCE?feature=shared

Please be aware these are just notes so details are not here. Only seek a professional and certified practitioner of Dry Needling.
| Trigger point dry needling: | |
| Head, Neck, and Orofacial | |
| Corrugator supercili muscle | Moves eyebro down at Yuyao “fish waist”, frontal headache |
| tx: pincer palpation, perpendicular in skin, downwards toward eye | |
| shallow and into muscle belly. | |
| Procerus | Wrinkles the brdice at nose, Yintang “Seal hall”, facial nerve VII, frontal headache |
| Pincer palpation, perpendicular, downward towards nose, into muscle belly | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/VHS6rNPd-DA?feature=shared | |
| Masseter Muscle | Closes the mouth, Trieminal n. cranial V v3 branch. Near ST7 Xiaguan “Lower hinge” |
| Needle perpendicular to the skin into muslce belly | |
| https://youtu.be/9n0rOb6hvow?feature=shared | |
| Temporalis muscle | Closes the mouth. Cranial N. V, trigeminal, v3 branch. GB3, GB7 |
| Temporal headache. Neelde perpendicular toward temporalis fossa. | |
| Caution: temporal artery | |
| https://youtu.be/7DX4sXTUCpI?feature=shared | |
| Zygomatic Muscle | Zygomatic bone to mouth, smiling, Facial n. VII, |
| SI18 Quanliao “Cheek Seam”, needle slanted or perpendicular. | |
| Medial Pterygoid muscle | Lower part of mandible, closes mouth, Trigeminal n.V |
| St6 Jiache “jaw bone” into muscle belly. Angle of mandible | |
| https://youtu.be/CguhaUIIc0g?feature=shared | |
| Lateral Pterygoid muscle | TMJ joint, trigeminal n. V, v3, |
| Near ST7, patient opens mouth, needle into the muscle belly towards the molar root. | |
| https://youtu.be/VYh0T2hcS1M?feature=shared | |
| Digastric muscle | Under the Chin, inferior border of mandible. Facial n. VII. Left and right side of Ren23 |
| Needle perpendicular to the mastoid notch, toward transverse process of atlas | |
| Caution jugular vein. Anterior or posterior belly can be needled. | |
| Neck and Shoulder muscles | |
| Trapezius: upper portion | External occipitus. Used in side bending, neck extention. CN XI (Accessory) C3-C4 |
| Prone or side lying: pincer palpitation, perpidicular. Anterior to posterior or vice versa. | |
| GB21 Jianjing, “Shoulder Well” | |
| https://youtu.be/WL691oJoo4A?feature=shared | |
| Levator Scapulae | dorsal tubercles of transvers process C1 to C4, extends, side bends neck. |
| Superior portion: near SI16 tianchuang (heavenly window) side lying | |
| Lower shoulder portion: near SI15 jian Zhong shu (middle shoulder) | |
| caution- pneumothorax. | |
| superior- posterior and medial angle | |
| https://youtu.be/bpRwegXdGRM?feature=shared | |
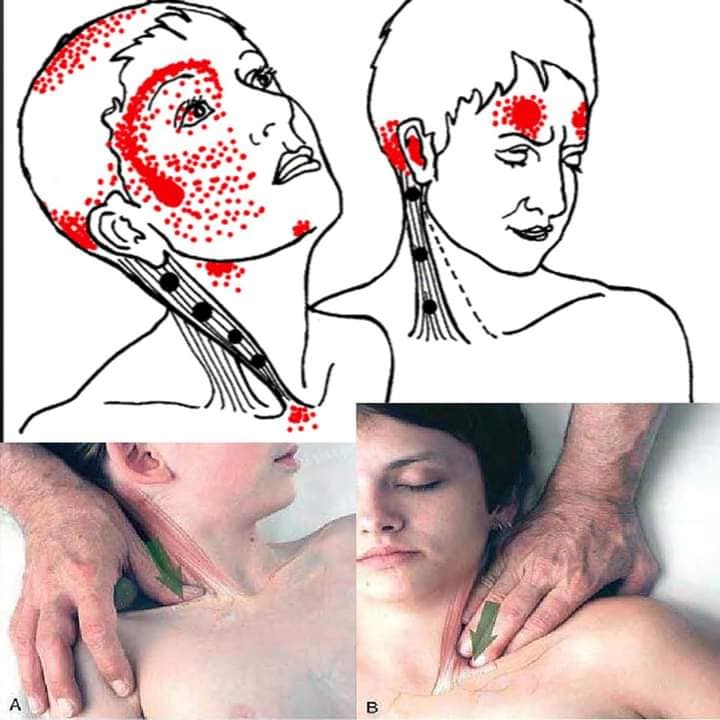
| Sternocleidomastorid muscle | Sternal and Clavicular, mastoid process, neck flexion/extension. CN XI, C2-C3. ST9 |
| Pincher palpation: obliquely downward into muscle belly. Carotid artery caution | |
| https://youtu.be/_2opxDY8Kgc?feature=shared | |
| Splenius Capitis muscle | C7 to T3-T4, extenstion, side bend, rotate neck. TB16 area |
| Needle side lying, toward mastoid process. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/JJ24XlTHZyw?feature=shared | |
| Splenis Cervicis muscle | Spinous process T2-T6 to C1-C3, extend and rote neck. Below BL10 area |
| Pincer palpation side lying, needle in a medial direction, anterior to posterior | |
| https://youtu.be/_BCJxw2C8Z4?feature=shared | |
| Semispinalis Capitis and Cervicis muscles | C7 and T1-T6 to occipital. Extention and rotation. |
| Side lying: pincer palpation, perpendicular from anterior to posterior | |
| https://youtu.be/njVmH83jtxs?feature=shared | |
| Suboccipital muscles | C1, C2. Extend of head. below BL10 |
| needle: side lying, between c1 and c2 toward patient opposite eye medially. | |
| https://youtu.be/-thao1ElN7Q?feature=shared | |
| Cervical Multifidi muscles | Cross 2 of 4 vertebral levels.C2 to C5, whereas inferior C2 to C7 |
| stabalize the neck, extenstion and rotatation. Hua tuo jia jie | |
| Needle prone, needle if patient reports deep pain in cervical joints. | |
| Avoid epidural and subaracnoid space, spinal cord. Lateral to medial direction. | |
| https://youtu.be/UOBtqZfZCEo?feature=shared | |
| Scalene muscles | C3 to C6 anterior scalene. Posterior not needled, too close to lung |
| used in side bend. Near KD27 area. Postior supior angle away from lung. Short needle. | |
| Needle: supine, perpindular about 3 cm over the clavical | |
| https://youtu.be/prIHP74BK7c?feature=shared | |
| Shoulder muscles | |
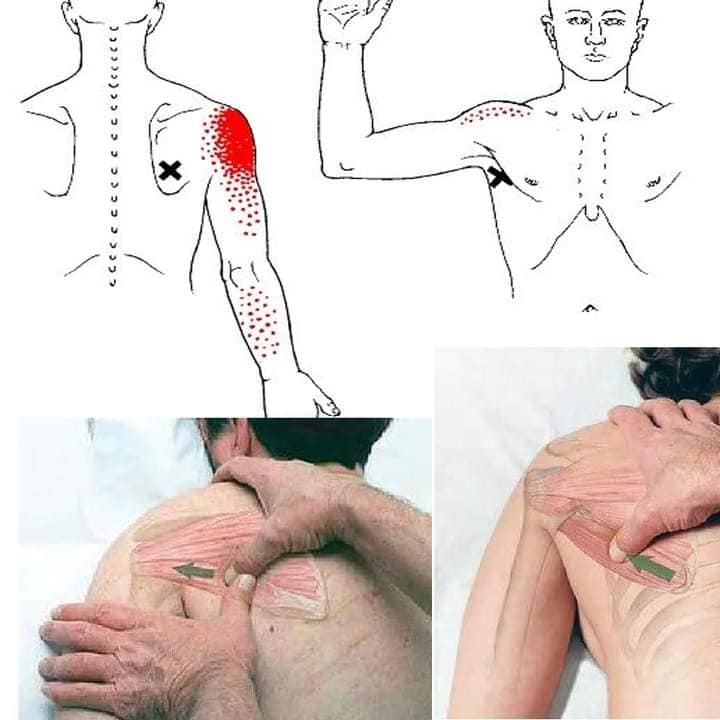
| Supraspinatus muscle | Supraspinatus fossa of the scapula insert superior facet of greater tubbercle of humerus. |
| abduction, stabalize humerus head, rotator cuff muscles all movement of shoulder | |
| prevents caudal dislocation during carry heavy suitcase. C5 and C6 nerve root, | |
| suprscapular n. , referred- mid-deltoid, lateral aspect arm, lateral epicondyle of elbow | |
| prone/side lying, access via upper trapezius muscle w/flat palpation w/ sufficient pressure | |
| localize TrP longitude to the frontal plane or posterior to the base of supraspinatus fossa | |
| Caution- apex of lung in front of scapula. LI16 area | |
| https://youtu.be/99iqRIIYJmA?feature=shared | |
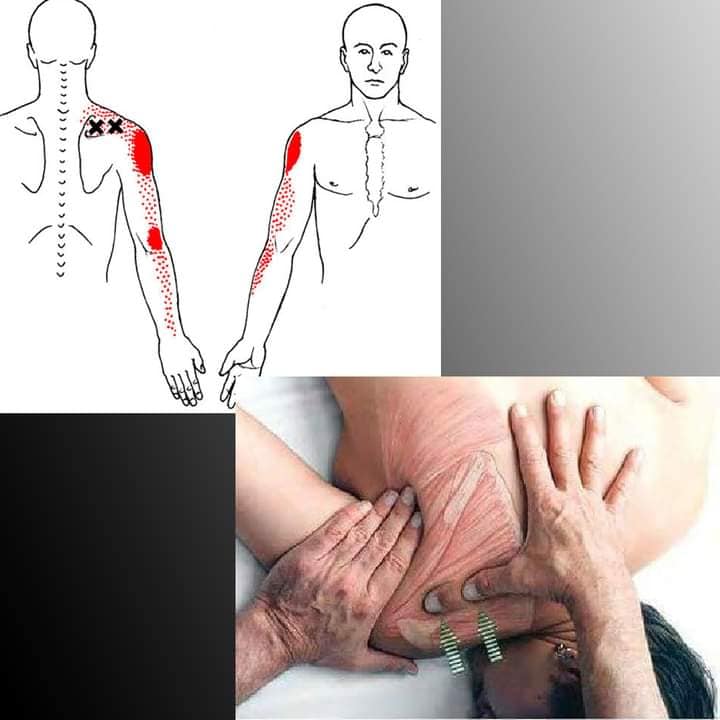
| Infraspinatus muscle | Infraspinatus fossa of the scapula and inserts at the dorsosuperior facet of the greater |
| tubercle of humerus. External rotation, stabalize humerus head, prevent upward migration | |
| suprascapular n., C5 and C6 nerve root. Symptoms of carpal tunnel. SI11 Tianzhong | |
| prone/side lying- needle toward the scapula, find TrP and do not needle deep | |
| https://youtu.be/TYHtnuo3XeI?feature=shared | |
| Teres Minor muscle | upper 1/2 lateral border of dorsal surface of scapula, insert dorsal facet of greater tubercle |
| below the isertion of the infraspinatus muscle. Same actions as infraspinatus | |
| but it can adduct upper arm. Axillary N. C5 to C6 nerve root. SI9 Jian Zhen “True shoulder” | |
| referred pain is in dorsal aspect of shoulder- numb/tingle ulnar aspect arm and hand | |
| caution pleura space and lung. | |
| needle prone, upper arm 90 degree TrP is just caudal to Glenohumeral joint. | |
| needle toward the lateral border of scapula. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/SU8Ll_quAQE?feature=shared | |
| Subscapularis muscle | Subscapular fossa insert to the lesser tubercle and reinforce transverse ligament |
| that overlies the bicipital sulcus.GB22 Yuanye “armpit abyss” | |
| Internal rotation with pectoral muscle, subscapular n. C5,C6,C7 n.roots | |
| Needle Axillary approach supine arm 90 degree abducted and 90 degree externally rotated. | |
| Needle away from the ribcage. Prone can be done. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/tNtA1oS6bNY?feature=shared |
| Deltoid Muscle | Origin lateral 1/3 clavicle, inset into deltoid tuberosity, anterolateral border of humerus |
| abduction of the upper arm, assist flexion and inner rotation, extension, external rotation | |
| Axillary n., C5, C6 n. roots. Near LI14, PC2, LU3, Si13, jianqian “front of shoulder” | |
| Anterior part in supine position, posterior part in prone. Can do side lying, needle | |
| into the taut band against the humerus | |
| https://youtu.be/Afc_5wAGvxs?feature=shared | |
| Teres Major Muscle | Origin: posterior surface of inferior angle scapula, latissimus dorsi (LT), insert medial lip |
| of bicipital groove. It assists LT in extension, internal rotation, and adduction of arm | |
| Lower subscapularis n., C6, C7 n. root. Si9 and Si11 is closest to it, but not same. | |
| Needle with arm slightly abducted, grasp muscle and needle anterior and lateral. | |
| Caution the ribcage. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/SU8Ll_quAQE?feature=shared | |
| Coracobrachialis muscle | |
| Rhomboid muscles | |
| Pectoralis Minor | Origin 3,4,5 Rib near costal cartilages and inserts at the coracoid process of scapula |
| with coracobrachialis and biceps brachii brevis. | |
| Moves scapula forward, back and inward, accessory respiration muscle. | |
| Medial pectoral n. C8,T1. LU1, LU2 area | |
| Supine position, upward and lateral towards coracoid process, shallow needle. | |
| Caution- ventral surface of rib cage, avoid intercoastal space, neurovascular bundle. | |
| Women should draw breast away from site. | |
| https://youtu.be/Ba3-Y1Ty53A?feature=shared | |
| Pectoralis Major | Crosses 3 joints: sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, glenohumeral |
| Dorsal origin is from sternal, coastal, and abdominal regions. | |
| Protects shoulder girdle, internal rotation adduction of arm, medial flexion across chest | |
| lateral pectoral n., C5 to C7 n. root. LU1, LU2 area | |
| Patient lies supine arm slightly abducted. Women should draw breast away from site. | |
| https://youtu.be/CaD4OmTicGc?feature=shared |
| Latissumus Dorsi muscle | origin from spinous process of lower 6 thoracic, all lumbar, iliac cres, aponeurosis to sacrum |
| Inserts at the medial edge of intertuberacule groove of humerus | |
| Extends, adducts, internally rotates arm, retraction of scapula, extends spine | |
| thoracodorsal n., C6-C8 n. root, pain can radiate to the 4 and 5 finger. | |
| Prone with arm off table, grasp muscle, palpate for taut bands, lift away from chest wall | |
| Caution- chest wall. Not near any acupuncture points | |
| https://youtu.be/eRQNd1oOKAY?feature=shared | |
| Can do side lying and supine as well. | |
| Biceps Brachii long head muscle. | Origin attaches to upper margin of glenoid fossa, short is from coracoid process of scapula |
| Insertion at radial tuberosity. Flexion of arm, abduction of arm, elbow flexion | |
| musculocutaneous n. via lateral cord C7,C8 | |
| Supine w/arm slightly flexed, grasp muscle, find taut bands, avoid neurovascular bundle | |
| caution radial n. near Lung 4 | |
| https://youtu.be/UebkZPJVI9w?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/nk4VkkoWoNo?feature=shared | |
| Tricepts Brachii long head | crosses shoulder joint, attaching to the scapula below glenoid fossa, the three heads |
| attach to the olecranon of the ulna via common tendon. TB12, TB13 area | |
| Adduction of arm at shoulder, rotation of scapula. Radial n. posterior cord C7,C8 | |
| Referred pain can be posterior shoulder, upper traps, dorsum of forearm. | |
| prone, side lying, pincer grasp, find taut bands, initiate a local twitch response. | |
| https://youtu.be/uc77oX4FNSE?feature=shared | |
| Subclavicular muscle | Under clavicle, attaches medially by a short thick tendon first rib, caudal aspect clavicle |
| Protraction of shoulder. Subclavian n. C5, C6 root. KD26/27 area | |
| referred pain can go to the forearm and hand radial side. | |
| Supine, needle toward maximum tenderness below clavical. | |
| caution- pneumothorax. | |
| https://youtu.be/1RD2Ii8MlRE?feature=shared | |
| Arm and Hand Muscles | |
| Coracobrachialis muscle | O: coracoid process, insert mid-portion of humerus. Assist flexion and adduction of arm |
| Musculocutaneous n., C5, C6 roots. Near HT1 Jiquan “summit spring”, PC2 | |
| supine position, flat palpation, perpendicular to skin medial to lateral upper 1/3 humerus. | |
| caution the neurovascular bundle located dorsally and medially to the muscle. | |
| https://youtu.be/jKten_cLS14?feature=shared | |
| Bicep Branchii short head | O: coracoid process of scapula to insert lesser tuberosity of the radius. HT2 Qingling Green spirit |
| flexion of the forearm at the shoulder, and assist supination of forearm | |
| Musculocutaneous n. lateral cord C5, C6. median n. runs anatomically medial to muscle belly | |
| Supine, needle with pincer palpation, perpendicular, medial to lateral side of short head | |
| toward the patient’s finger. Caution: neurovascular bundle. | |
| https://youtu.be/V8Owxo52Q2A?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/2PNS3eqYvb4?feature=shared | |
| Triceps Brachii muscle (lower) | crosses shoulder joint, attaching to the scapula below glenoid fossa, the three heads |
| extends the forearm at elbow. Radial n., C7 C8 spinal roots. TB11, TB 12 areas | |
| Prone, flat palpation, perpendicular insert, lateral to medial side, toward posterior of humerus. | |
| pincer palpation. Caution the radial n. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/udQcJsU705M?feature=shared | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/XTXf39bcXQ8?feature=shared | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/lYnbKs8sVX8?feature=shared | |
| Anconeus muscle | origin is side of olecranon and dorsal surface ulna, insert lateral epicondyle |
| extension of forearm at the elbow. Radial n. spinal roots C7 and C8 | |
| Prone with forearm flexed 45 at the elbow, flat palpation, perpendicular to ulna bone | |
| Li10 acupoint Area. Zhoushu extra point. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/XfwlL0fLWpc?feature=shared | |
| Brachialis muscle | O: distal 2/3 of humerus and inserts at the coracoid process of the ulnar tuberosity |
| Flexes forearm at elbow. Musculocutaneous n. C5, C6 spinal root.PC3 area lower part upper arm | |
| Supine, elbow relaxed and slightly flexed. Lateral aspect of arm. Caution: Neurovascular bundle | |
| https://youtu.be/kw7SxCO6Ao0?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/ccqBSNtrB7Y?feature=shared | |
| Brachioradialis muscle | O: upper 2/3 of supracondylar ridge of the humerus attaching of distal radius at styloid process. |
| flexes forearm at elbow. Radial n. C7, C8 | |
| Supine, pincer palpation, medial or lateral aspect towards patient fingers. | |
| Caution the radial n.Li10 area | |
| https://youtu.be/85dpe9MeRik?feature=shared | |
| Supinator muscle | O: lateral hueral epicondyle, radial collateral ligament, annular ligament and the supinator |
| crest of the ulna. Insert over radial tuberosity and upper third radial shaft. | |
| Supinates the forearm, assist flexion of elbow | |
| Radial n. C7, C8. LI 10, LI9 region of arm. | |
| Supine: needle in flat palpation, perpendicular at dorsal forearm, upper 3rd of radial bone. | |
| https://youtu.be/JN-fGtC62io?feature=shared | |
| Wrist and fingers Extensor muscles | |
| Extensor Carpi radialis longus | this group originates form lateral ridge of humerus, lateral epicondyle, attack to second metacarpals |
| Extensor Carpi radialis brevis | They extend all muscles and deviate the hand at the wrist to radial or ulnar side. |
| extenosr digitorum communis | Spinal roots of C7 C8. These are in the LI and TB meridian areas of forearm |
| Extensor carpi ulnaris | needle supine, pincer palpation |
| https://youtu.be/cyNSuSY5mZA?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/zBAvCYrOJcI?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/p6Z3aUYGvQg?feature=shared | |
| Pronator teres muscle | Humeral head origin and ulnar head origin, inserting over the radius distally |
| Pronates the forearm and assists pronator quadratus. Median nerve, brachial plexus from C6 C7 | |
| Carpal tunnel affected. Supine: forearm supinated1-2 cm below the medial condyle. | |
| Near Ht3, PC3 area caution the median n., needle perpendicular toward the ulna or radius | |
| https://youtu.be/6d3rztL4d_s?feature=shared | |
| Wrist and finger flexor muscles | |
| Flexor Carpi radialis | Origin from supracondylar ridge of the humerus bone, medial epicondyle, insert to metacarpal bones |
| Palmaris Longus | These muscles felx and deviate the hand and wrist radial or ulna side |
| Flexor Digitorum superficialis | Median nerve, C6, C7, brachial plexus C8,T1. Caution the median n. |
| Flexor Digitorum profundus | https://youtu.be/uu3a0-X3O48?feature=shared |
| flexor carpi ulnaris | https://youtu.be/0Ja_ixoOqIo?feature=shared |
| https://youtu.be/P2ZAze-F57o?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/oWvbiQDHZdc?feature=shared | |
| Flexor Pollicus longus | origin is proximal part of radius, insert to base of distal phalanx of the thumb. PC channel |
| Extensor Pollicus longus | O: dorsal surface of the ulna bone and the interosseous membrane to base of distal phalanx of thumb. TB5 area |
| Abductor pollicus longus muscles | Origin is ulnar side of middle third of radius, insert into the radial side of base of first metacarpal bone. Lu10 area |
| , flex, extend, abduct. Brachial plexus spinal roots C6, C7, radial n. | |
| Patient supine- insert perpendicular to the skin towards dorsal aspect of the middle third radius. | |
| caution the median n. | |
| https://youtu.be/wJjd4w5w05I?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/Oq4Cy5zji9c?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/uRtKhDdB4hY?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/9ngHeOoZ8qA?feature=shared | |
| Adductor Pollicus | originates in the carpometacarpal region of the index and middle fingers, base of proximal phalanx of the thumb |
| Opponens pollicus | trapezium bone of wrist and flexor retinaculum in heel of hand to first metacarpal bone |
| Flexor pollicus brevis | trapezium, trapezoid and capitate bones and the flexor retinaculum to the palmar aspect of the first metacarpal |
| Abductor pollicus brevis | originates in the scaphoid bone and flexor retinaculum to insert the lateral aspect of first metacarpal and sesamoid |
| functions: adduct, , opposite, flex, abduct | |
| Innervation C8, T1 brachial plexus C6 C7. Areas LI4, LU9, LU10, | |
| needle with short and thin needle, patient supine, forearm pronated, avoid tendons | |
| https://youtu.be/l3WAFTqwdWY?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/iRb7XEjk13A?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/5QbHFSmyqPQ?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/uRtKhDdB4hY?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/mhMBAZcC0cU?feature=shared | |
| Interosseous | dorsal or palmar lie in between the adjacent metacarpal bones |
| lumbricals | attach proximally to the 4 tendons in the palm, distally radial side of each 4 fingers |
| abductor digiti minimus | arise proximally from the pisiform, attaches distally to ulnar side, base of first phalanx of pinky |
| abduction, adduction. C8, T1, brachial plexus C6, C7. TB3, TB4 area, SI3, SI4 area | |
| Needle: supine with flat palpation, perpendicular, dorsal aspect toward finger | |
| https://youtu.be/VDD6Sd9SkH0?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/vvm4fkNkiDM?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/MjJb_YPuOrg?feature=shared | |
| Trunk Muscles | |
| Pectoralis major | Attachments in medial clavicular, sternal, and coastal fibers. All fibers converge laterally to the |
| lateral lip of the intertuberous suluc of the humerus.Acupoints include Lung, St, KD ,SP, Ren, PC channel points | |
| Adduct and internally rotate the humerus. Used in forceful inhale. | |
| Lateral pectoral n. (c5-C7) medial pectoral n. C8-T1, C7-C8 coastal secion. | |
| *Caution- pneumothorax*. Patient supine, women move breast out of area, shallow depth. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/gkInQ_KTU8o?feature=shared | |
| Rhomboid Major and minor | major: spinous process and supraspinatus ligament of T2 to T5, descend medial border of scapula |
| Minor: distal ligmaentun nuchae and the C7 to T1 to the base of triangular surface of the medial end scapula spine. | |
| Retract the medial border of scapula superiorly and medially. | |
| Dorsal scapular n. C4 C5, upper trunk of brachial plexus. BL 13,14,15 area | |
| Patient prone, secure taught band with index and middle fingers, needle away form ribs. | |
| *Caution- pneumothorax*. Block intercoastal space with fingers. | |
| https://youtu.be/2bXMELmWlLs?feature=shared | |
| Serratus posterior superior muscle | distal portion of the nuchal ligament C7 to T3 attaching to 2-5 upper boarder of ribs. |
| 2-5 intercoastal nerves. BL11, BL12 area | |
| Prone- secure a taut band over a rib, fingers blocking intercoastal space, needle at angle toward rib, avoid lung | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/5Cc7hGJyfCc?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/A-bClRtAETQ?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/bBTs1k0DtCA?feature=shared | |
| lower- | https://youtube.com/shorts/mh0MQ199wqk?feature=shared |
| Middle Trapezius muscle | Attaches medially to the spinous process and the supraspinatus ligament of C7 to T3 attach scapula spine and acromion |
| Scapular adduction, adduct scapula, stabilization during flexion and abduction | |
| Cranial n. XI, 3rd and 4th cervical n. supply sensory fibers. Si12, Si13 area | |
| Patient prone, secure taught band with index and middle fingers, needle away form ribs. Can use pincer grip. | |
| *Caution the lungs* | |
| https://youtu.be/MB4mVDqU1y0?feature=shared | |
| Lower Trapezius muscle | attaching medially to spinous process at T6 to T12 region, attach at aponeurosis on the medial end of the scapular spine |
| inner rotation, adducts and depress scapula | |
| Cranial n. XI, 3rd and 4th cervical n. supply sensory fibers | |
| Patient prone, secure taught band with index and middle fingers, needle away form ribs. Can use pincer grip. | |
| https://youtu.be/MB4mVDqU1y0?feature=shared | |
| Latissumus Dorsi (trunk portion) | origin from spinous process of lower 6 thoracic, all lumbar, iliac cres, aponeurosis to sacrum |
| Inserts at the medial edge of intertubercular groove of humerus | |
| Extends, adducts, internally rotates arm, retraction of scapula, extends spine | |
| thoracodorsal n., C6-C8 n. root, pain can radiate to the 4 and 5 finger. | |
| Prone with arm off table, grasp muscle, palpate for taut bands, lift away from chest wall | |
| Caution- chest wall. acupuncture points BL18, bl19, bl20 area | |
| Serratus Anterior muscle | Coastal attachments and inserts into scapula to upper boarder of 8,9,10 ribs. SP21 area |
| Prime mover is reaching motion. | |
| Long thoracic n. C5-C7. *Avoid lung** when needling. | |
| Patient on side: secure taught band with index and middle fingers blocking intercoastal space, needle away from ribs. | |
| https://youtu.be/G2_86m3_Bgk?feature=shared |
| Longissimus Thoracis muscle | Tips of the transverse process of thoracic vertebrae ribs 3 through 12 between their tubercles and angles, |
| Blending with iliocostalis lumborum, attaching to entire posterior surface of the transverse process | |
| of lumbar vertebrae to middle layer of thoracolumbar fascia.Like the upper back first line of BL channel | |
| Extend and laterally flex the spine against gravity. Flex forward or laterally with gravity. | |
| patient lies prone, identify TrP with flat palpation, insert superior to TrP, shallow angle. AVOID LUNG. | |
| https://youtu.be/aPhus5xS7Ow?feature=shared | |
| Iliocostalis Thoracis and Lumborum | attachment proximally to the upper border of the angles of the lower six ribs, medial to the tendoms of the insertion |
| of iliocostalis lumborum and to superior border of angles of the upper six ribs and transverse process of C7 | |
| Lumborum attaches to the inferior border of the angles of the lower six ribs. Both attach inferiorly to | |
| the anterior surface of a broad aponeurosis.Aponeurosis attaches to the spinous process of the lumbar and T11/12 | |
| and laterally to the medial aspect of the iliac crest and lateral sacral crest blending with sacrotuberous and dorsal | |
| sacroiliac ligaments. | |
| these muscles extend and laterally flex the spine against gravity, they contract eccentrically as spine flexed forward. | |
| Prone: lower back second line of BL channel | |
| https://youtu.be/lGEd94mZx0s?feature=shared | |
| Multifidus muscles | thoracic and Lumbar |
| Fasciculi that attach most caudally to the back of sacrum and to posterior superior iliac spine and dorsal sacroiliac | |
| ligaments. In the lumbar spine, they attach to the mammillary processes and in the thoracic spine to the transverse | |
| processes. The fasiculus run superiorly and medially, attaching to the base or tip of the spinous process of the | |
| vertebrae above.the supieor fasciculi attach three levels up, the deeper connect two levels up, and the deepest are | |
| adjunct to the vertebrae. Huatojiajie area points | |
| Stabailization of the spine, Extend the spine, unilaterally, rotate the vertebrae to the contralateral side. | |
| Patient prone, muscle palpitated with flat palpitation in the valley next to the spinous processes | |
| needle is perpendicular and in a caudal direction toward lamina of veterbral body. | |
| https://youtu.be/aChLTg8Q-NA?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/0eZOQHQZoAQ?feature=shared | |
| Serratus Posterior inferior muscle | deep to the latissimus dorsi muscle, medially it attaches to the spinous process of T11 to about L3 |
| it passes obliquely in a superior and lateral direction and divides into four flat digitations. The digitations attach to the | |
| inferior, posterior surfaces of last 4 ribs, lateral to their angles. | |
| Used in ipsilateral trunk rotation and lower thoracic extension. Second bladder channel line | |
| Innervation ventral rami of T9 to T12 thoracic spinal nerves. | |
| Prone patient, the needle is directed shallow angle toward 9,10,11,12 rib. PROTECT the LUNG, cover intercoastal areas. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/mh0MQ199wqk?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/rGLVtwXYq0s?feature=shared | |
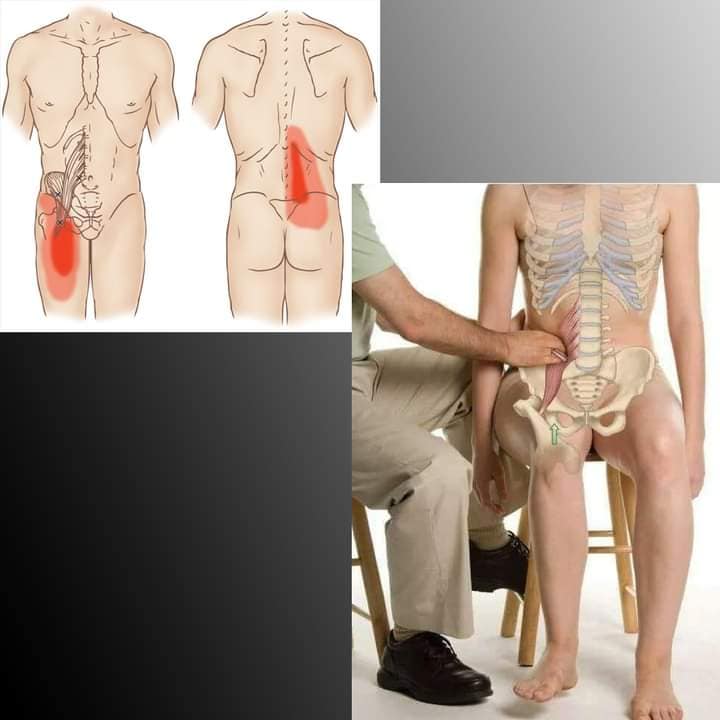
| Quadratus Lumborum | attaches inferiorly by aponeurotic fibers to the iliolumbar ligament and adjacent portion of iliac crest |
| it attaches superiorly to the medial half of the lower border of the 12th rib and to the transverse process of L1 to L4 | |
| Assists inspiration and forced exhalation, extending the spine, contralateral bending. | |
| 12 thoracic n. and upper 3 lumbar spinal n. (Bladder channel area) | |
| Needle side lying, identify the mucles with flat palpation, L4 is best to palpate it as it is under latissumus dorsi. | |
| longer needle is required, striaght dwon, avoid the kidney | |
| https://youtu.be/rOTrmLI-iqw?feature=shared | |
| Rectus Abdominus muscle | attaches inferiorly along the crst of the pubic bone via a medial and lateral tendon. Medial tendon interlaces |
| with the contralateral muscle and attaches to the symphysis pubis. Superiorly it attaches to the 5,6,7 coastal | |
| cartilages. The paired recti are separated in midline by linea alba. | |
| side bending and trunk rotation, used in exhalation, defecatio, micturition, parturination, coughing and vomiting. | |
| Intercoastal n. 7 through 12. (Ren, Kidney, Stomach channel areas) use a smaller needle to not go deep. | |
| Supine, pul muscle toward you creating a wall,needle medialy toward linea alba, tangent ab wall. | |
| upper- needle parallel to ribs, lower- needle toward public bone. Avoid abdomnial cavity and Lung. | |
| https://youtu.be/_PyvrkD-D5A?feature=shared | |
| External and internal obliques | External is largest and superficial of the lateral abdominals. Attaching superiorly to the external, inferior border of |
| the lower 8th ribs, interdigitizing with the latissumus dorsi and serratus anterior. Fibers from lower two ribs | |
| pass vertically to attach to the anterior half of iliac crest. Middle and upper fibers pass obliquely and medially | |
| and caudally to join abdominal aponeurosis. The internal lies deep as do the transverse abdominus. | |
| These help the trunk rotation and side bending. used in exhalation, defecatio, micturition, parturination, | |
| coughing and vomiting. InnervationT8 to T12, iliohypogastric and iliolingual n. from L1. | |
| Supine or side lying, grasp abdominal wall, avoid abdominal cavity. | |
| https://youtu.be/7v0gFxR8PSs?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/pgTqRN2kACg?feature=shared | |
| Hip, Pelvis, and thigh | |
| Hip muscles | |
| Gluteus Maximus muscle | Origin: psterior aspect of the ilium, the lower part of the sacrum and coccyx inferior and lateral across the |
| greater trochanteer to the iliotibital band of tensor fascia lata and glueteal tuberosity. | |
| Hip extension, lateral rotation, stabailize iliotibial tract. | |
| Inferior glueteal n. L5, S1, S2. Near huanzhong area | |
| Prone: flat palpation, perpendicular, avoid sciatic n. | |
| https://youtu.be/6d0pLpdCa7o?feature=shared | |
| Gluteus Medius muscle | Between gluteus Maximus and tensor fascia latea. Origin is between posteror and anterior |
| gluteal lines of the ilium and inserts on the lateral border of the greater trochanter. Bursa lies under the tendinous | |
| portion over the surface of trochanter. | |
| Hip abduction and medial rotation. Insuffiency is positive Trendelenburg test. | |
| Superior gluteal n. L4,L5 and S1. GB/Shao yang side | |
| Patient prone or side, flat palpation, perpendicular,avoid sciatic n. | |
| https://youtu.be/x7nq7D9qfyI?feature=shared | |
| Gluteus Minimus muscle | Deep to gluteus medius, between anteror and inferor gluteal lines of the anterior aspect of ilium, inserts |
| on the anterior aspect of greater trochanter, has a bursa between tendon and insertion at grater trochanter. | |
| Hip abduction, medial rotation. | |
| Superior gluteal n. L4, L5, S1. | |
| Prone or side: flat palpation, perpendicular, caution the gluteal vessels and nerves. | |
| https://youtu.be/DspE4ijPD6c?feature=shared | |
| Tensor Facia Latae muscle | From the outer aspect of iliac crest and th anterior superior iliac spine, between the gluteus medius and |
| satorious muscle, and from the deep surface of the fascia lata. Insert between two layers of the | |
| iliotibial band of the fascia latae of the middle and upper thirds of the thigh. | |
| Extends knee w/lateral rotation of leg, assists flexion. Abduction and medial rotation of hip | |
| Superior gluteal n. L4. L5, S1. | |
| Supine or side, flat palpation, perpendicular. | |
| https://youtu.be/fW57QNxjG4s?feature=shared | |
| Obturator Internus muscle | Anterior lateral wall of inner pelvic brim, rim of obturator membrane, covering most of the obturator foramen, |
| the pelvic surfce of the obturator internus and it sfascia form the anterior lateral wall of true pelvis | |
| attaching to greater trochanter I close proximity to gemelli muscles. Betweem BL35 BL36 area | |
| laterally rotate hip. L5, S1. referred pain in vagina, anoccygeal region, posterior thigh. | |
| Lithotomy position, palpate. Avoid pudendal canal nerves and vessels. | |
| https://youtu.be/lyiC2Kbf4pc?feature=shared | |
| Obturator Externus, Gemellus interior | flat triangular muscle that covers external surface of obturator membrane and adjacent bone of the ischial and |
| pubic rami laterally and upward to trochanteric fossa of the femur. | |
| Lateral rotation of hip, hip and pelvis stability. L3-L4, L5, S1 | |
| Prone, found deepr and more posterior to the trochanter. GB 30 area | |
| Quadratus Femoris muscle | Flat quadrilateral muscle that originates at the upper part of the external aspect of the ischial tuberosity and |
| inserts above the middle of the trochanteric crest of femur. | |
| Lateral rotate of thigh, L5, S1. BL36 area. | |
| Prone: palpate greater trochanter and ischial tuberosity, find TrP by palpation, parallel to sciatic n. (caution) | |
| https://youtu.be/5ePdgGxUs4Y?feature=shared | |
| Piriformis muscle | Originates at the anterior surface of the sacrum at S2 to S4 where it passes through and fills the greater sciatic |
| foramen. It inserts on the upper border of the greater trochanter of the femur. | |
| External rotation of thigh or abduction if thigh is flexed. L5, S1, and S2. Near BL29, BL30, GB30 area. | |
| Prone or side lying, avoid sciatic n., bony landmarks of greater trochanter and sacrum S2 to S4. | |
| https://youtu.be/G_3dpYPUKtA?feature=shared | |
| Pelvic Diaphragm muscles | |
| Ischiocavernosus muscle | Inferior lateral aponeurosis over the curs of the penis or clitoris to the medial aspect of the pubic ramus and ischium |
| used to compress the veins to maintain penis or clitoris erection. Puidendal n. S2,S3,S4 | |
| Lithotomoy position. Avoid perineal branch nerves and vessels. Near hui yin, lateral to sex organ | |
| https://youtu.be/LVazkGgtlfA?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/sLa6sEGkfWQ?feature=shared | |
| Bulbospongiosus muscle | muscle originates at the superficial perineal membrane and dorsal penile or clitoral aponeurosis and attaches |
| at the perineal body in women, and at the medial raphe over the corpus spongiosum. | |
| Vascual engorgement of the penis or clitoris, constrict vagina in women, empty urine and ejaculation in men. | |
| Pudendal n. S2 to S4 | |
| Lithotomoy position, | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/hJFiGyB_4jg?feature=shared | |
| superficial and deep transverse perinei | Originiating from the ischim at the inferior ramus and run medially to the lateral aspect of the vagina or medial |
| line in men. The superficial transverse perinei is a narrower muscle, blends with fibers of sphincter inferiorly | |
| and bulbospongiosus superiorly at the central tendon of perineal body. | |
| Stabilize central tendon of perineal body. Prudendal n. S2 to S4. Hui Yin area | |
| Lithotomy position, palpate. Avoid pudendal canal nerves and vessels. | |
| Pubococcygeus m. pelvic diaphragm | Originating from the back of the publis and the anterior part of the obturator fascia. Its direction is posterior in a |
| horizontal fashion to the coccyx and the most inferior aspect of the sacrum. At the posterior insertion two | |
| pubococcygei muscles come together and form a thick, fibromuscular layer. The puborectalis muscle slings | |
| around the rectum to aid in defication. Pubovagalis muscle arise for the anterior fibers to the perineal body | |
| to aid vaginal wall support. The levator prostate muscle is the corresponding muscle in the male. | |
| Function to to constrict and elevate the lower end of rectum and vagina, support pelvic viscera. | |
| Pudendal nerve, 4th sacral branch. Pain: in perineun, coccygeal, vagina, rectal, pelvic girdle. Sitting, bowel movement. | |
| neeedle side lying, 90 degree pillow between knees. | |
| https://youtu.be/rQQSqLCF12g?feature=shared | |
| Iliococcygeus muscle pelvic diaphragm | originates from the ischial spine and posterior part of the tendinous arch of the pelvic fascia, inserts into the |
| last two segments of the coccyx and anococcygeal raphe. Usualy thin and fibrous tissue. | |
| Function to constrict and elevate the lower end of rectum and vagina, support pelvic visera | |
| Pudendal nerve, 4th sacral branch. Pain: in perineun, coccygeal, vagina, rectal, pelvic girdle. Sitting, bowel movement. | |
| neeedle side lying, 90 degree pillow between knees. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/LVprIGeDUxA?feature=shared | |
| Coccygeus muscle of pelvic diaphragm | Triangular shape muscle that originates from the spine of the ischium and sacrospinous ligament, and inserts into |
| the margin of the coccyx and inferior lateral angle of the sacrum. | |
| Function to constrict and elevate the lower end of rectum and vagina, support pelvic visera | |
| 4th and 5th sacral nerves. | |
| Prone with pillow under stomach for comfort or side-lying with hips flexed 90 w/pillow between knees. | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/JNsGC7tldP0?feature=shared | |
| Thigh muscles | |
| Adductor longus muscle | Fan shaped muscle originates from front of public bone between the crest and symphysis and inserts in |
| the linea aspera in the middle one-third of the femur. | |
| Adduction and medial rotation of the thigh as well as a hip flexion with an extended hip. | |
| Obturator n. L2 to L4. SP11 area | |
| patient is supine with knee flexion and hip external rotation. Caution femoral artery and sciatic n. | |
| https://youtu.be/4Mai9xZVij0?feature=shared | |
| Adductor Brevis muscle | Origin is posterior to the pectineus and adductor longus with a narrow attachment of the external aspect of the |
| body and inferior ramus of the pubis between the gracilis and obturator externus. It inserts posterior | |
| laterally into the femur from the lesser trochanter to the linea aspera and directly behind the brevis and upper part | |
| of longus. | |
| Adduction and medial rotation of the thigh as well as a hip flexion with an extended hip. | |
| Obturator n. L2 to L3. | |
| patient is supine with knee flexion and hip external rotation. Caution femoral artery and sciatic n. | |
| https://youtu.be/1XDHR_1x9tg?feature=shared | |
| Adductor magnus muscle | Large fan shaped muscle origin from the inferior ramus of the pubis, conjoined ischial ramus and the |
| inferior-lateral aspect of the ischial tuberosity. Insert with horizontal, oblique and vertical fibers at the gluteal | |
| tuberosity and linea aspera deep to the brevis and longus. | |
| Adduction and medial rotation of the thigh as well as a hip flexion with an extended hip. | |
| Obturator n. L2 to L4., tibial division of sciatic. | |
| patient is supine with knee flexion and hip external rotation. Caution femoral artery and sciatic n. | |
| https://youtu.be/ZG6Z0EL2Bxg?feature=shared | |
| Pectineus muscle | the muscle is a flat quadrangular that originates at the pectin pubis and the pubic bone between the iliopectineal |
| eminence and the tubercle and attaches at lesser trochanter. | |
| Adducts the thigh and flexes it on the pelvis. | |
| Innervation of femoral n. from L2-L3. near Liv10, liv11 | |
| Patient supine with slight hip rotation, palpate femoral artery | |
| https://youtu.be/y5eaLFf-poU?feature=shared | |
| Gracilis muscle | Origin is from the medial margins of the lower half of the body of the pubis, the inferior pubic ramus |
| and the ischial ramus and inserts to the upper part of the medial tibia just bvelow the medial condyle. | |
| Flexion and medial rotation of the leg and adduction of the thigh. | |
| Obturator n. (L2-L3) | |
| Patient supine with slight hip external rotation, flat palpation. | |
| https://youtu.be/rlzmHCNscdw?feature=shared | |
| Rectus femoris muscle | fusiform muscle that originates from the anterior iliac spine, from a groove about the acetabulum, and from the |
| capsule of the hip joint. The muscle inserts at the base of the patella via a thick flat tendon. | |
| Knee extension, hip flexion. Innervation Femoral n. L2 to L4. Near ST31, ST32 area | |
| Patient supine. Avoid femoral artery. | |
| https://youtu.be/FN3mNinhuSI?feature=shared | |
| Vastus Lateralis muscle | Origin is in the upper part of intertrochanteric line, antieror and inferior borders of greater trochanter, |
| attaching to a flat tendon to the base and lateral border of patella. | |
| Knee extention and patellar tracking. Femoral n. (L2-L4) Between ST and GB channels (Tung points) | |
| Patient supine or side-lying. | |
| https://youtu.be/TqvVBrxzPy4?feature=shared | |
| Vastus medialis muscle | Origin lower intertrochanteric line, linea aspera, medical intramuscular septum, medial supracondylar line |
| tendons of the adductor magnus and longus muscles, insert medial border of patella. | |
| Knee extension, patellar tracking. Femoral n. L2-L4. SP10 to SP11 area | |
| Supine position | |
| https://youtu.be/-rT3VjDvja0?feature=shared | |
| Vastus intermedius muscle | Under rector femoris, originates at the anterior and lateral surface of the upper two-thirds of the femoral shaft |
| and from the lower part of the lateral intermuscular septum. Inserts with the deeper fibers of quad tendon | |
| and the lateral aspect of patella, and lateral condyle of the tibia. | |
| Knee extension, Femoral n. (L2-L4), ST21 area. | |
| Patient supine | |
| https://youtu.be/cvtV5V38gN0?feature=shared | |
| Genu Articularis muscle | Small muscle under retus femoris. Retraction of suprapatella bursa during knee extension |
| Femoral n. L2- L4, needle under rectus femoris tendon. Ex point Jianxi above heding, needle to bone then propagate | |
| https://youtu.be/pBGTYUWL0VE?feature=shared | |
| Biceps femoris muscle | long head of the biceps femoris muscle originates from the upper part of the ischial tuberosity via a tendon it |
| shares with the semimembrinosus muscle. Short head from lateral lip of linea aspera. | |
| Two heads emerge at the distal end of the muscle and attach to fibular head, and later epicondyle of the tibia | |
| flexion of knee. Sciatic n. (l5 to S2). Patientprone: bolster under anklespalpate and find TrP flat palpation | |
| caution: sciatic n. oblique posterior to anterior. BL37 area, lateral both side of the point | |
| https://youtu.be/HV-VGSMgci8?feature=shared | |
| Semimembranosus and Semitendinosis | Originates with a flat tendon from the supralateral part of the ischial tuberosity, the biceps femoris |
| and semitendinosus muscles, travels deep to the semitendinosus muscle to divide into five components | |
| and insert at the tubercle of the mdial tibial condyle, the mdical margin of the tibia, the fascia over the | |
| popliteal muscle and lateral femoral condyle where it forms much of the oblique popliteal ligament. | |
| flexion of knee. Sciatic n. L5 to S2, through tibial division. Tong points, Liv and KD channel area of thigh | |
| prone with bolster, look for TrP flat palpation. | |
| Semimembranosus | https://youtu.be/z03GCARLm9Y?feature=shared |
| Semitendinosis | https://youtu.be/xy4Ygvk3qHc?feature=shared |
| Between BL and KD channel areas | |
| Sartorius muscle | Longest muscle in the body originating from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) crosses over the thigh |
| obliquely to the medial side, and inserts at the proximal medial surface of the tibia anteriorly to the insertions | |
| of the gracilis and semitendiosus and to the capsule of the knee joint. | |
| flexion of leg at the knee, hip flexion, abduction, lateral rotation at thigh | |
| Femoral n. L2-L3. Patient supine, needle tangently. Avoid femoral artery, vein, nerve. | |
| Leg and foot | |
| Popliteus muscle | Obtuse and triangluar in shape. Laterally and proximally it attaches to the lateral condyle of the femur, |
| to the posterior capsule of the knee joint, to the lateral meniscus, and to the head of the fibula. | |
| Medially and distally it attaches to the posteromedial surface of the tibia. | |
| medial rotation of tibia. Lateral rotation of femur, knee flexion. Tibial n. L4-S1. SP9 area | |
| side lying: hip and knee flexed to 90 degree. Muscle is palpated. Avoid saphenous n. | |
| https://youtu.be/yNPY_QuuMxU?feature=shared | |
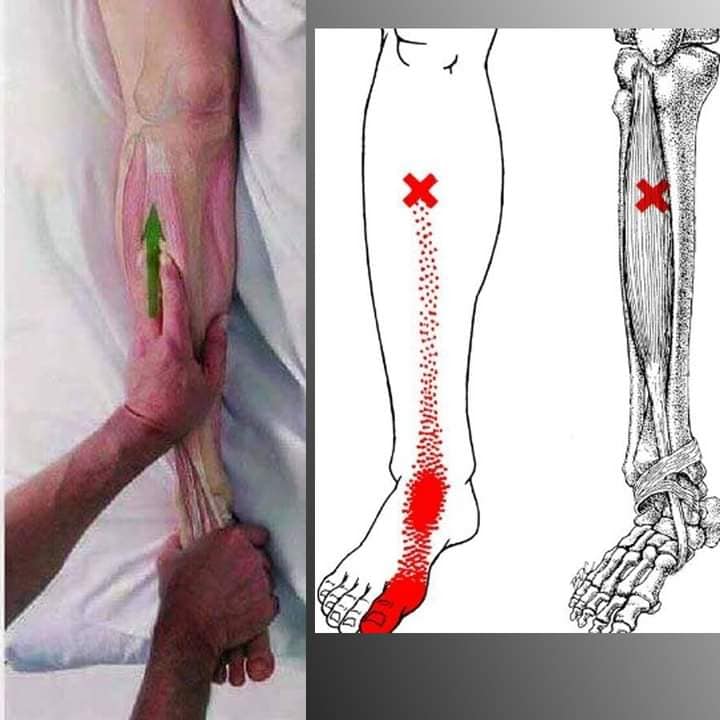
| Gastronemius muscle | lateral and medial head. Proximally each head anchors to the corresponding condyle of the femur and to |
| the capsule of the knee joint. Distally both heads insert into the achilles tendon, attach posterior calcaneus bone. | |
| Plantar flexion and supination of foot. Knee and ankle stability. Tibial n. S1, S2 | |
| Prone position, pincer palpation medial, flat palpation lateral, caution sciatic n. | |
| Lateral and medial to BL40, BL 55. BL56, BL57 | |
| https://youtu.be/wJFs65ffNuk?feature=shared | |
| Plantaris muscle | attaches to the upper part of lateral condyle of the femur. Distally, its long tendon anchors to the medial |
| aspect of the calcaneus, blending with the fibers of the achilles. | |
| plantar flexion and inversion of foot. Tibial n. L5- S2. Needle similar to lateral head of gastronemious. | |
| Caution the Tibial an peroneal n and vessels. | |
| https://youtu.be/-s2QOrv54-Q?feature=shared | |
| Soleus muscle | Originates in the posterior aspect of the head and proximal third of the fibula, in the popliteal line |
| of the tibia and in the tendinous arch between both bones. They attach distally to a superficial tendinous | |
| shet into achilles and posterior part of calcaneus. | |
| Plantar flexion and inversion of foot. Tibial n. L5- S2. Near BL58 medially. | |
| Prone using pincher between two fingers, needle toward fibula. | |
| https://youtu.be/E2whn_fnhLE?feature=shared | |
| Flexor Digitorum longus muscle | proximally the muscle attaches to the posteror aspect of the tibia and to the deep layer of the fascia cruris. |
| distally its four tendons attach to the base of the distal phalanx of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th toes. | |
| Plantar flexion, inversion, adduction of foot. Tibial n L5-S1. SP channel SP6, SP7 area | |
| Patient lying on involved side. | |
| https://youtu.be/slDWtp8XV3c?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/wSo6QtAI0HA?feature=shared |
| Tibialis Posterior muscle | Proximally this muscle orginiates on the inner posterior borders of the tibia and fibula and on the interosseous |
| membrane. Distally, the tendon attaches to the bases of the 2,3,4 metatarsals, the three cuneiforms, | |
| the cuboid, the tuberosity of the navicular, the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus. | |
| Supination (inversion and adduction) and plantar flexion. Tibial posterior n. L5-S1. SP7, SP8 area | |
| Deep insertion but caution the tibial n. and peroneal n. and vessels. | |
| https://youtu.be/Eg7xTIcgqJk?feature=shared | |
| https://youtu.be/3B0B5w3jJGo?feature=shared | |
| Flexor hallicus longus muscle | Originiating in the lower 2/3 of the posterior surface of the fibula and in the interosseous membrane. |
| it’s tendon anchors to the base of the distal phalanx of big toe. | |
| Plantar flexion and inversion of the fot. Flexion of big toe. Tibial n. L5-S2. | |
| Patient prone, , use flat palpation, look for tenderness. BL channel, tong achilles point area | |
| https://youtu.be/PKW7FSYRK3A?feature=shared | |
| Peroneus longus and brevis | Arises from the head and upper 2/3 of the lateral surface of the body and fibula and intermuscluar septa between |
| it and the adjacent muscles. Inserts in the ventral and lateral sides of the base of the first metatarsal bone | |
| and the cuneiform. They stabailze the leg upon the foot, plantar flexion and eversion. | |
| Peroneal n. (L4-S1). Around ST36 and GB34 area (longus) GB36, GB37 (Brevis) | |
| Patient lying on uninvolved side, hips and knee flexed 90 degree.palpate with flat technique. Caution- peroneus n. | |
| https://youtu.be/ON0s8OFXfOs?feature=shared | |
| Peroneus Tertius muscle | Origin is from the lower half of the aneterior aspect of the fibula and in the crural intermuscular septum between |
| it and the peroneus brevis muscle. Inserts in the medidorsal surface of the base of the metarsal bone of the | |
| 5th digit in base of 4th metatarsal. For eversion and dorsiflexion of the foot. | |
| Near the GB40 area. | |
| Patient supine TrP found with flat palation. | |
| https://youtu.be/_ORpy6vnDhw?feature=shared | |
| Tibialis anterior muscle | Origin is upper 2/3 of the lateral surface of tibia and insert into the medial and plantar aspect of |
| medial cuneiform bone and into the medial surface of the base of the first metatarsal bone. | |
| Dorsi flexion and supination of the foot. Deep peroneal n. L4-S1. ST36, ST37 area | |
| patient in supine position,TrP is located with flat palpation, medial towrd tibia. | |
| https://youtu.be/RmPU0pT8I0g?feature=shared | |
| Extensor digitorum Longus | The muscle originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia, from the 3/4 of the anterior surface of the body |
| of the fibula; from the upper part of the interosseous membrane and from the intermuscluar septa between | |
| it and the tibialis anterior muscle on the medial side, and the peroneal muscles on the lateral side. | |
| distally it divides into the 2,3,4 phalanges of the 4 lesser toes. | |
| Dorsi flexion and eversion of the foot. Deep peroneal n. L4-S1. ST channle ST39/ST40 area | |
| Patient supine, TrP with flat palpation. Caution the peroneal n. and vessels. | |
| https://youtu.be/168bh95YKRk?feature=shared | |
| Extensor hallicus Longus muscle | origin middle 2/4 of the anteromedial surface of the fibula medial to the origin of the extensior digitorum longus |
| muscle, it also originates from the interosseous membrane. Its tendon attaches distally to the base of the distal | |
| phalanx of the great toe and through an expansion of the tendon, usally the proximal phalanx. | |
| Dorsi flexion and inverison, great toe. Deep peroneal n. L4-S1. Between ST40 and ST41 | |
| Patient supine, TrP with flat palpation. Caution the peroneal n. and vessels. | |
| https://youtu.be/dHnCK_7eiw8?feature=shared | |
| Extensor digitorum Brevis and | Both anchor proximally to the superior aspect of the calcalneus, to the lateral talocalcaneal ligament and |
| Extensor hallicus brevis | to the cruciate crural ligament. Distally, the extensor hallucis brevis inserts in the dorsal surface of the base |
| of the first phalanx of the great toes, and the extensors digitorum brevis ends in 3 tendons | |
| that insert into the lateral sides of the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus muscles 2,3,4th toes. | |
| Extend the toes. Deep peroneal n. L5, S1. GB41 area | |
| patient supine. Avoid deep peroneal n. | |
| https://youtu.be/An7rYSd9kd4?feature=shared | |
| abductor hallucis muscle | Proximally this muscle attaches to the medial process of the tubersoity of the calcaneus, to the laciniate ligament |
| to the plantar aponeurosis, and to the intermuscular spetum between it and the flexor digitorum muscle. | |
| distally its tendon inserts together with the medial tendon of the flexor hallucis brevis muscle, plantar side big toe. | |
| flexion and abduction of the big toe. Medial plantar n. L5, S1. Near KD2 area | |
| Patient lying on involved side. | |
| https://youtu.be/hr0mpE3Q3Jw?feature=shared | |
| Abductor digiti miimi muscle | Proximally themuscle attaches to the lateral process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus, to the inferior |
| surface of the calacneus between the two processes of the tuberosity, to the front part of the medical process, to the | |
| plantar aponeurosis, and to the intermuscular septum between it and the flexor digitorum brevis. | |
| distally it s tendon inserts with the flexor digiti minimi brevis into the fibular side of the base of 5th toe. | |
| Abduction and flexion of the proximal phalanx of the 5th toe. Lateral plantar n. s1, S2. BL64, BL65 area. | |
| Patient lying on involved side. Find taut band with flat palpation., use pincer grip. Caution nerve. | |
| https://youtu.be/zS6W5t7hDhw?feature=shared | |
| Flexor digitorum brevis muscle | Proximally, the muscle arises from the medial process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus, from the plantar fascia, |
| and from the adjacent intermuscular septa. Distally, it divides into 4 tendons, one for each of the four lesser | |
| toes. At the base of the first phalanx, each tendon divides into two slips, to allow passage of the corresponding | |
| tendon of the flexor digitorum longus, the second split of tendon inserts to second phalanx. | |
| Flexion of rist phalanx of 4 toes. Medial plantar n. L5, S1. Below KD1 in middle of foot before heel. | |
| Patient prone, caution the plantar vessels and nerves. | |
| https://youtu.be/S9OU_e5hTCQ?feature=shared | |
| Quadratus plantaris muscle | Muslce has two heads, separated by long plantar ligament. Medial and larger head originates in the medial |
| concave surface of the calcaneu. Both join at a acute angle and end in a flattened band with inserts into the | |
| lateral margin and upper under surfaces of the tendon of the flexor digitorum longus. | |
| flexion of the 4 toes. Lateral plantar n. S2, S3. Master Tongs Brain point area | |
| https://youtu.be/X6406M9wzAA?feature=shared | |
| https://youtube.com/shorts/OJdUtP3wsU0?feature=shared | |
| Flexor Hallucis Brevis muscle | Proximally the floexor hallucis brevis anchors to the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone |
| to the contiguous portion of the 3rd cuneiform and to the prolongation of the tendon tibialis posterior which it | |
| is attached to the bone. It then divided into two portions, which insert distally into the medial and lateral aspect | |
| of the base of the first phalanx of big toe. | |
| flexion of big toe at metatarsaophalangeal joint. Medial plantar n. L5, S1. SP3 SP4 area | |
| patient on involved side, palpate via flat palpation. | |
| https://youtu.be/448Wfnam1Ws?feature=shared | |
| Adductor Hallucis muscle | Muscle has 2 heads. The oblique head arises from the bases of rthe 2,3,4 metatarsal bones and fromsheath of the |
| tendon of peroneus longus. Distally it inserts together with the lateral side of the base of the first phalanx of big toe. | |
| Adduction of the big toe, flexion proximal phalanx of big toe. Lateral plantar n. S2, S3. Liv3 point area | |
| https://youtu.be/snCLfoJPb_c?feature=shared | |
| Dorsal and Plantar interossei muscles | 4 dorsal interossei and 3 plantar interossei in foot. |
| Dorsal: https://youtu.be/QKbA9RSIhmw?feature=shared | |
| Dorsal abduct the 2,3,4 toes. Plantar: adduct 2,3,4, 5th toes. Bafeng points | |
| Lateral Plantar n. s2,S3, | |
| Patient supine, TrP with flat palpation. | |
| https://youtu.be/4reB4C4_lA0?feature=shared |
Dry Needle and Anatomy Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLZKMPKSntzQQua643yhcO9qjcKT3ifR0F